MCQ of RADIOGRAPHY STUDENTS
Q1. Radiation protection concept in Radiology practice.
A. Optimisation for radiation protection (OPR)
B. As Low as Reasonably Achievable (ALARA)
C. Both A and B
D. None
2. Radiation is defined as
A. Energy is transmitted from one location to another.
B. Heat is Transmitted from one location to another.
C. Charge is transmitted from one location to another.
D. All of the above.
Q3. Which of the following is not done in case of brain tumour ?
A. CT scan
B. MRI
C. Skull X-RAY
D. Lumbar puncture
Q4. In MRI, the strength of MRI is
A. 0.6 Tesla
B. 1.5 Tesla
C. 3 Tesla
D. Both B and C
5.Best view for sella turcia is
A. Open mouth
B. Oblique view
C. AP view
D. Cone Lateral view
6. Best method to diagnose bronchiectasis is
A. X-Ray
B. Bronchography
C. MRI
D. HRCT
7. EM radiation depends on
A. Wavelength
B. Velocity
C. Intensity
D. Penetrating power
8. All are true except
A. X-ray is an invisible ray
B. X-ray having a short wavelength
C. X-ray is ionizing power
D. X-Ray can be used to see the object.
9. What is the Gamma energy of annihilation radiation used in PET SCAN?
A. 0.511KeV
B. 0.500KeV
C. 0.01KeV
D. 0.25KeV
10. Hecto is
A. 102
B. 103
C. 104
D. 10-3
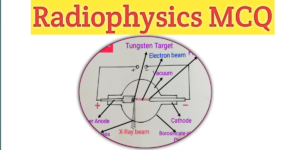
11. In an X-ray tube electrons travel from
A. Cathode to Anode
B. Anode to Cathode
C. Cathode to sidewall
D. Anode to sidewalls
12. Full form of DSA –
A. Digital Source Angiography
B. Digital Substance Angiography
C. Digital Substraction Angiography
D. Data Subtraction Angiography
13. Y view is for
A. Skull
B. Shoulder
C. Scapula
D. Foot
14. TLD is used for
A. Radiation monitoring
B. Radiation protection
C. Both A & B
D. None
15. 1 Sievert is equal to
A. 1 rem
B. 10 rem
C. 100 rem
D.1000 rem
16. High kVp is mostly used in
A. CXR
B. Pelvis
C. Skull
D. Spine
17. Glass window of X- RAY tube is made of
A. Lead
B. Tin
C. Beryllium
D. Aluminium
18. Barium swallow is done for
A. Stomach
B. Esophagus
C. Rectum
D. Large intestine
19. The value of CT number is determine by
A. Matrix size
B. Slice thickness
C. kV
D. Tissue density
20. In IVP, in children contrast is given as
A. 1-2 ml/ kg
B. 2-3ml/ kg
C. 3- 4 ml/kg
D. No contrast is given
21. What is the CT number for blood?
A. 40 – 50
B. 60 – 90
C. 100 – 200
D. 1000
22. Dexa scan is done for
A. Measure bone density
B. To view spine fracture
C. To look at the blockage
D. None
23. Stryker view is done for
A. Chest
B. Temporal bone
C. Shoulder
D. Styloid process
24. MRI is invented by
A. Purcell
B. Rutherford
C. Hounsfield
D. Roentgen
25. Atomic number of gadolinium is
A. 65
B. 64
C. 89
D. 92
26. Solide state detector is used in which generation
A. 1st
B. 2nd
C 3rd
4. 4th
27. NaI detector system which generation used ?
A. 1st
B. 2nd
C. 3rd
D. Both A and B
28.Xenon detector system used in which generation ?
A. 1st
B. 2nd
C. 3rd
D. 4th
29.Translate and rotate detector used in which generation
A. 1st
B. 2nd
C. 3rd
D. Both A and B
30.Rotate – rotate detector used in which generation?
A. 1st
B. 2nd
C. 3rd
D. 4th
31. Only Rotate tube system was used and the detector assembly does not rotate, which generation used?
A. 1st
B. 2nd
C. 3rd
D. 4th
32. CTDI stands for
A. CT density index
B. CT dose index
C. CT diameter index
D. None of the above
33. CT number for fat is
A 100
B. 1000
C. -40 -60
D. -100
34.ALARA Principal is base for
A. Time
B. Distence
C Shielding
D. All the above
35. Raw data of MRI after the acquisition is temporarily saved in
A. K Space
B. ADC
C. Magnetic coil
D. None
36. The mathematical calculation used to convert raw data into CT images is
A. Fourier transformation
B. Shell data Technique
C. Analog-digital technique
D. None
37. Which sensing material is used in TLD
A. Barium sulfate
B. Calcium sulfate / Lithium fluoride
C. Sodium iodide
D. None
38. Barium meal is the study for
A. Kidney
B. Stomach
C. Rectum
D. None
39.Horseshoe kidney is related to
A. Foot
B. Liver
C. Kidney
D. Skull
40. HSG stands for
A. Hysterosalpingography
B. Hystero salivarygarphy
C. Hyster sigmoidgraphy
D. Hepetosalpingography
41. Advantage of DR system is
A. Save time
B. Save expenditure on the film
C. Immediate readout
D. All of the above
Another Set of Radiophysics MCQ-
1. Boxer fracture is related with
A.Leg
B.Skull
C.Thumb
D.Little finger ( meta carpal)
2. Atomic number of Tungsten is ?
A. 74
B. 53
C. 73
D. 76
3. Before doing contrast study which lab test is mandatory?
A. Renal function test
B. PTI
C. Hemoglobin
D. All of the above
4.Hounsfield( HU )of fat …
A. 1000
B. + 1000
C. -60 to – 100
D. 0
5. Which is not the severe contrast reaction?
A. Nausea
B. Severe Bronchospasm
C. Laryngeal oedema
D. Loss of consciousness
6.Frog leg view is done for ?
A. Skull
B. Shoulder
C. Hip
D. None
7. What is DWI sequence?
A. Diffusion weighted imaging
B. Diffusion weight image
C. Diffused way image
D. None
8. REM full form
A. Radiation equivalent man
B. Rapid eye movement
C. Rapid eye man
D. Roentgen equivalent man
9. ERCP full form
A. Endoscopically retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
B.Endoscopic retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
C. Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography
D. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography
10. CT number of water is …
A. 100
B. 10
C. 0
D. 1000
11. CT number of blood is …
A. 40
B. 60
C. 60- 90
D. 50 – 70
12. X-ray tube consists
A. Anode
B.Cathode
C.Berryllium window
D. All of the above
13.1 inch is equal to ..
A.253mm
B.254mm
C.255mm
D.256mm
14. In MRI ,TOF is ..
A. Time of flight
B. Time of fight
C. Train of fan
D. None
15. Common femoral artery is branch of
A. Abdomen arota
B. Iliac artery
C. Tibia artery
D. None
16.Exposure to ionizing radiation can be limited ?
A. With the use of shielding
B. By increasing distance from the source
C. By limiting the time exposed to the radiation
D. All of the above
17. The lowest rate of ultrasound absorption occurs in..
A. Fat
B. Air
C. Bone
D. Lung
18. Melting point of tungsten in degrees Celsius?
A. 3370
B. 337
C.7383
D. 3372
19. Modern X-ray tube has …
A. 1 filament
B. 2 filament
C. 1 anode
D. Both A and B
20.Aromic number of Tin is
A. 51
B. 50
C. 52
D. 53
21. The amount of radiation intensity reduced if proper shielding is done..
A. To the half value layer of material
B. To the 10th value layer of the material
C. Both A and B
D. None
22. What is the full form of BEIR ?
A. Biological effects of ionizing radiation
B. Bio effects of ionizing radiation
C. Bio effects of ion radiation
D. Biological effect of ionizing radiation
23. TLD stands for …
A.Thermo luminescent dosimeter
B. Thermo light dosimeter
C. The light dosimeter
D. None
24. Beam hardening artifact is associated with …
A. MRI
B. CT Scan
C. USG
D. None
25. The skin dose is the …
A. Entrance skin dose
B. Exposure to the entrance surface of the skin
C. Absorbed dose below the skin surface
D. A and B are correct
26. The unite of RF power density is …
A. Watts
B. Watts per kilogram
C. Watts per square meter
D.Coulombs per kilogram
27. Diffusion weighted imaging measure…
A. Motion to water molecules
B. Motion of cells
C. Chemical composition of cells
D. Ratio of water to fat
28.Converts x-ray into light …
A. Backing layer
B. Crystal layer
C. Phosphor layer
D. Lead layer
29.Atlas is a part of …
A. Cervical spine
B. Dorsal spine
C. Lumber spine
D. All
30. For trauma cervical spine which view taken ?
A. Lateral view
B. AP view
C. Both A and B
D. None
31. Posterior fossa lesion are best seen in …
A. CT
B. MRI
C. DSA
D. Bone scan
32 .Routine abdominal imaging in USG…
A. 3- 5 MHz
B. 5- 7 MHz
C. 6.5 – 7.5 MHz
D. 5.5 – 6.7 MHz
33.Wavelength of x-ray …
A. 0.1- 1A°
B.0.2 – 2 A°
C. 2- 3 A°
D. 00.1- 0.1A°
34. Grid ratio is …
A. Height of grid / thickness of interspace material
B. Height of grid / grid strip thickness
C. Height of grid / grid diameter
D. None
35. Dose limit for the eye per year ( NCRP)
A. 500 mSv
B. 150 mSv
C. 50 mSv
D. 5 mSv
36.Dose limit of Gonads is
A. 00.5mSv
B. 0.5 mSv
C.0.005 mSv
D. 0.02mSv
37. In manual processing , developing takes …
A.15 sec
B. 22 sec
C. 5 min
D. 10 min
38. What is the DICOM full form ?
A. Digital imaging and communication
B. Digit imaging and community
C. Both A and B
D. None
39. Open MRI is most suitable in …
A. Claustrophobic patient
B. Children
C. Both A and B
D. All
40. Different type of coils use in MRI are ..
A. Shim coil
B. Gradient coil
C. RF coil
D. All
41. Permanent magnet used in MRI is made of
A. Iron
B.Gunmetal
C. Alnico ( Aluminium,Nickel,Cobalt)
D. None
42. Disadvantages of MRI …
A. High cost
B.Claustrophobia
C.Long imaging time
D. All
43.For screening of breast scan which is best technique…
A. CT
B. MRI
C. Mammography
D. X- Ray
44. CT number for bone is …
A. 100
B. 0
C.+1000
D. + 50
45.Investigation of choice for a lesion of the temporal bone is …
A. X-Ray
B. CT
C. USG
D. MRI
46.Hounsfield units depends on
A. Election density
B. Mass density
C. Effective atomic no
D.Attenuation
47.Which gives maximum radiation dose to the patient?
A. Chest
B. MRI
C.CT
D.Bone scan
48. The Innominate bone is located in the …
A. Middle cranial fossa
B. Posterior cranial fossa
C. Foot
D. Pelvis
49.Beam hardening artifact is related to…
A.MRI
B.CT
C.Fluoroscopy
D.All
50.Highly radiosensitive normal tissue…
A.Bone
B.Muscle
C.Brain
D.Gonads
51.CT scan room is shielded by …
A. Tungsten
B.Steel
C. Lead
D. Glass
Some important objective question and answer –
1. Radio graphic film has …….parts .
A. Two
B. Three
C. Four
D. Five
2. Adhesive layer is present between ..
A.Base and base
B.Base and super coat
C. Base and emulsion
D. Emulsion and emulsion
3. The thickness of Radiographic film is …
A. 0.05 mm
B. 0.4mm
C. 0.25mm
D. 1.5mm
4. Radiographic film has …..
A. Single coated layer
B. Double coated layer
C. Both
D. All of the above
5. Heart of Radiographic film is …
A. Emulsion
B. Base
C. Flexibility
D. Stability
6. The science dealing with properties of matter and energy is ….
A. Physiology
B. Physics
C.Pathology
D. Psychology
7.The smallest subdivision of an element is…
A. Molecule
B. Atom
C. Proton
D. Electron
8.The Electromagnetic radiation travels in …
A. Air
B. Presence of oxygen
C. Water
D. Vacuum
9.The energy associated with the motion of an object is called …
A. Electrical
B. Kinetic
C. Potential
D. None of the above
10.The material in which the current flows rapidly is known as …
A. Insulator
B. Semi conducter
C. Conductor
D. Semi insulator
11. The substance which does not allow electrons to flow is called ..
A. Conductor
B. Semi conducter
C. Insulator
D. Semi- insulator
12. The Visible light consists of ….
A. Two colours
B. Five colours
C. Seven colours
D. Four colours
13. The glass envelope of x-ray tube is made of …
A. Steel
B. Borosilicate or Pyrex glass
C. Ordinary glass
D. Fiber glass
14. Most of the rotating anodes revolve with a speed of ……. Regulation per minute.
A. 3400
B. 3000
C. 1500
D. 4500
15. The penitration of x-ray beam is directly related to ..
A. Selection of mA
B. Selection of kVp
C. Distence
D. Time of exposure
16.The area of anode disc on which the bombardment of electrons takes place …
A. Focus
B. Stem
C. Rotor
D. Spot
17. The % of amount of heat produced in an X-ray tube is …
A. 1%
B. 30%
C. 90 %
D. 99%
18. Which of the following will increase the radiation dose to the patient …
A. Use of collimator
B. Use of high Kv and low mAs
C. Use of low Kv and high mAs
D. Use of cones
19. Who has invented Computerized tomography is ….
A. Roentgen
B. Godfrey Hounsfield
C. Madam Curie
D. Bucky
20. The normal range of human hearing …
A. 0 to 20 Hz
B. 20 to 20,000 Hz
C. 20,000 to 50,000Hz
D. Above 50,000Hz
21.The Filter used in diagnostic x- ray tubes are made of …
A. Aluminum
B. Copper
C. Tin
D. Lead
22.The most frequent error in the use of grid is …
A. Improper grid ratio
B. Improper grid type
C. Improper positioning
D. None
23.Modern ( 4th generation ) CT scanner used …
A. 4800 detectors
B. 100 detectors
C. 30 detectors
D . 4 detectors
24.Minimum Anode heating capacity for CT tube is ….
A. 1 MHU
B. 2 MHU
C. 0.5 MHU
D. 0.25 MHU
25. Minimum anode heating capacity for spiral CT tube is ….
A. 1.5 MHU
B. 2.5 MHU
C. 3 MHU
D. 4 MHU
26.TLD used for personal monitoring in India is ….
A. LiF
B. CsI
C. CaSO4: Dy (3:1)
D. AgBr
27. The lateral curvature of vertebral column is known as …
A. Lordosis
B. Scoliosis
C. Kyphosis
D. Sarcoidosis
28. Breast Bone is ….
A. Scapula
B. Sternum
C. Clavicle
D. Humerus
29. Digestion of protein start from ….
A. Mouth
B. Esophagus
C. Stomach
D. Duodenum
30. The suture which join two parietal bone …
A. Lambdoid
B.Coronal
C. Saggital
D. None
31.The fluid containing cavities in the brain is known as …..
A. Sinuses
B. Ventricles
C. Spinal card
D. Frontanales
32.The area where Coronal suture and saggital suture meet is known as ….
A. Sinuses
B. Ventricles
C Fontanalle
D. Lambdoid
33.The most sensetive cells to ionizing radiation are …
A. Bone cells
B. Muscle cells
C. Nerves cells
D. Reproductive cells
Full form –
ERCP- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
MRCP- MR Cholangiopancreatography
RF – Radiofrequency effect
Gd- DTPA – Godolinium – Diethyl Triamine Panta Acetic acid. ( Magnevist, Ultravist ), Generally Godolinium chelate hota hai .
Spiral / Helical CT scan – Continuous source rotation, table translation, and data acquisition, this data multiple slices covering the volume of the patient.
I hope you like this post- MCQ of RADIOGRAPHY STUDENTS.
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found
that it is truly informative. I am going to watch out for brussels.
I’ll be grateful if you continue this in future.
A lot of people will be benefited from your writing.
Cheers!